The Complete Guide to Autoimmune Diseases

According to Johns Hopkins Medical, autoimmune diseases affect nearly 3% of the American population. But what is an autoimmune disease, exactly? When the human body attacks its own cells and tissues, the condition is known as an autoimmune disease. In autoimmune diseases, the body fails to differentiate between native and foreign cells such as bacteria and viruses. Because of this, the body releases antibodies that attack healthy native cells.
Autoimmune diseases may lead to the abnormal growth of organs, tissue deterioration, and alterations in organ functioning. Blood vessels, skin cells, red blood cells, endocrine glands, connective tissues, muscles, and joints can all be affected by autoimmune disease. In this blog, we’ll discuss everything you need to know about autoimmune diseases, including symptoms, treatment, and more.
Types of Autoimmune Diseases

Rheumatoid Arthritis
It is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system produces antibiotics that affect the body’s joints. Symptoms of this include joint pain and soreness, swelling, redness, deformities in the joints, and joint stiffness. Medications, home remedies, and dietary changes help in controlling rheumatoid arthritis. This disease can be detected using the rheumatoid factor test, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, anti-citrullinated protein antibody test, and antinuclear antibody test.
Graves Disease
Graves disease is a type of autoimmune disease that occurs as a result of hyperthyroidism, in which the body produces thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins. Hand tremors, unexplained fatigue, rapid heart rate, muscular weakness, swelling in the thyroid gland, disturbed sleep, and hearing intolerance are some of the symptoms associated with this disease. Should you suspect you might have Graves Disease, blood tests, thyroid-stimulating hormone tests, radioactive iodine uptake tests, and thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin tests may be necessary.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
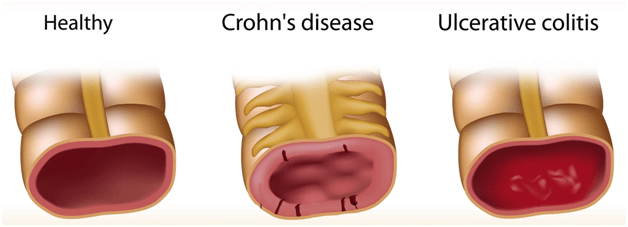
There are two types of autoimmune inflammatory bowel diseases, including Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. Inflammatory bowel diseases affect the intestinal walls by causing inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, large intestine, and rectum. Some of the major symptoms include the occurrence of diarrhea, bleeding ulcers, stomach pain, abnormal weight loss, cramps in the stomach, and anemia. This autoimmune disease may lead to malnutrition, fistula, bowel obstruction, and colorectal cancer if left untreated. To gain a diagnosis, your doctor will either take a stool sample or perform a colonoscopy, capsule endoscopy, etc.
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune disease in which the body attacks the myelin that affects the central nervous system. Associated symptoms include fatigue, numbness of limbs, difficulty balancing the body, optic neuritis that causes blurry vision, blindness, double vision, speech problems, tremors, and sleep problems. MRI scans, optical coherence tomography, visual evoked potential tests, and spinal taps are some of the tests used for diagnoses. Sadly, there are very few treatment options for this disease, however, medications and disease-modifying therapies typically prove effective.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic Arthritis is a condition wherein skin cells rapidly replicate, leading to the formation of red patches and skin swelling. UptoDate explains that there are 6 new diagnoses per every 100,000 people each year. Common symptoms include swelling in tender joints, scaly skin patches, swelling in the toes and fingers, extreme fatigue, nail pitting, eye redness, and eye pain. In some cases, spinal pain and stiffness are also visible. Psoriatic arthritis treatment comes in the form of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biological drugs.
Type 1 Diabetes
Another type of autoimmune disease is type 1 diabetes, in which the endocrine gland and the pancreas become damaged, ultimately leading to a decrease in the production of insulin. Insulin is essential for the body to breakdown and utilize glucose. Because of this decrease in insulin, the glucose levels in the blood rise above normal. If you suspect you may have this disease, excessive hunger, the frequent urge to urinate, fatigue, dry skin, nausea, excessive thirst, and blurred vision are all common symptoms. To treat type 1 or juvenile diabetes, insulin injections, medications, and tuberculosis vaccinations prove to be quite helpful. Finally, the major method of controlling type 1 diabetes is through dietary control.
Addison’s Disease
Addison’s disease occurs due to abnormal functioning of the adrenal cortex, leading to the unbalanced release of adrenal hormones. The symptoms that relate to this disease include nausea, tiredness, vomiting, depression, abnormal heart rate, loss of appetite, behavioral problems, hyperpigmentation, hypoglycemia, and sexual dysfunction. To treat Addison’s disease, medications and alternative therapies are required in most cases.
Autoimmune Diseases Concluded

Autoimmune diseases occur when the human body attacks its native cells and tissues. From the blood vessels to the skin, red blood cells, endocrine glands, connective tissues, muscles, and joints–autoimmune diseases can affect all areas of the body. If you find yourself experiencing such general symptoms as unexplained tiredness, trouble concentrating, redness and swelling in affected areas, skin rashes, muscular pain, and numbness in limbs, you may consider getting tested. To get set up with an appointment, contact the experts at 24-7Labs today.




